【Lab Objectives】
1. To master the concept of local properties and configuration optimization methods of BGP.
2. Local selection of properties for the default value is 100; the higher value of the path will be the preferred option.
3. Local priority properties, decided best path to leave this self-government system.
【Lab Topology】
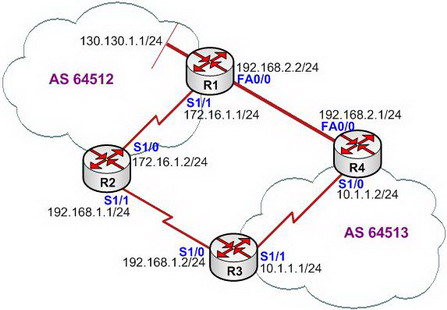
【Lab Steps】
1. Configure the router’s IP address, and use the Ping command to confirm the connect’s interoperability of each router.
2. Configure the BGP protocols of all routers. Due to the convergence of BGP is slow, after configured the BGP, to wait for some time.
3. Check the routing table of R3.
|
R3#show ip route
Gateway of last resort is not set
172.16.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets B 172.16.1.0 [20/0] via 192.168.1.1, 00:01:06 10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets C 10.1.1.0 is directly connected, Serial1/1 130.130.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets B 130.130.1.0 [20/0] via 192.168.1.1, 00:01:06 C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, Serial1/0 B 192.168.2.0/24 [200/0] via 10.1.1.2, 00:00:11 |
4. Check the routing table of R4.
|
R4#show ip route
Gateway of last resort is not set
172.16.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets B 172.16.1.0 [20/0] via 192.168.2.2, 00:02:18 10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets C 10.1.1.0 is directly connected, Serial1/0 130.130.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets B 130.130.1.0 [20/0] via 192.168.2.2, 00:02:18 B 192.168.1.0/24 [200/0] via 10.1.1.1, 00:02:18 C 192.168.2.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 |
5. In theory, all the routes that the BGP chosen are the best, but after observe the topology carefully, it is the Fast Ethernet between R1 and R4, and the speed reaches 100MB, while the next hop that R3 chosen to reach network 130.130.1.0/24 is 192.168.1.1. 2. it needs to go through the serial links of two wide area networks.
6. Check the BGP database information list of R3.
|
R3#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 7, local router ID is 192.168.1.2 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i – internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale Origin codes: i – IGP, e – EGP, ? – incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path * i10.1.1.0/24 10.1.1.2 0 100 0 i *> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i * i130.130.1.0/24 192.168.2.2 0 100 0 64512 i *> 192.168.1.1 0 64512 i * i172.16.1.0/24 192.168.2.2 0 100 0 64512 i *> 192.168.1.1 0 0 64512 i *> 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i * 192.168.1.1 0 0 64512 i *>i192.168.2.0 10.1.1.2 0 100 0 i * 192.168.1.1 0 64512 i |
7. Check the BGP database information list of R4.
|
R4#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 9, local router ID is 192.168.2.1 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i – internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale Origin codes: i – IGP, e – EGP, ? – incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path * i10.1.1.0/24 10.1.1.1 0 100 0 i *> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i * i130.130.1.0/24 192.168.1.1 0 100 0 64512 i *> 192.168.2.2 0 0 64512 i * i172.16.1.0/24 192.168.1.1 0 100 0 64512 i *> 192.168.2.2 0 0 64512 i *>i192.168.1.0 10.1.1.1 0 100 0 i * 192.168.2.2 0 64512 i *> 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i * 192.168.2.2 0 0 64512 i |
8. By comparing the BGP database of router R3 and R4, just need to adjust the the value of the local priority that router R4 has learned, because BGP will prefer to choose the route which has local higher values priority.
9. To configure the router R4, and adjust the priority of the local property value as 200.
|
R4(config)#router bgp 64513 R4(config-router)#bgp default local-preference 200 R4(config-router)#exit R4(config)# |
10. Check the BGP database of R3.
|
R3#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 10, local router ID is 192.168.1.2 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i – internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale Origin codes: i – IGP, e – EGP, ? – incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path * i10.1.1.0/24 10.1.1.2 0 200 0 i *> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i *>i130.130.1.0/24 192.168.2.2 0 200 0 64512 i * 192.168.1.1 0 64512 i *>i172.16.1.0/24 192.168.2.2 0 200 0 64512 i * 192.168.1.1 0 0 64512 i * i192.168.1.0 192.168.2.2 0 200 0 64512 i *> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i * 192.168.1.1 0 0 64512 i *>i192.168.2.0 10.1.1.2 0 200 0 i * 192.168.1.1 0 64512 i |
11. Check the routing table of R3 once again.
|
R3#show ip route
Gateway of last resort is not set
172.16.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets B 172.16.1.0 [200/0] via 192.168.2.2, 00:06:41 10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets C 10.1.1.0 is directly connected, Serial1/1 130.130.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets B 130.130.1.0 [200/0] via 192.168.2.2, 00:06:41 C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, Serial1/0 B 192.168.2.0/24 [200/0] via 10.1.1.2, 00:26:51 |
12. On R3, the next hop is 192.168.2.2 when reaches the subnet 130.130.1.0/24, because the next hop will not be changed when BGP notifies the route to the IBGP’s peer, such a mechanism known as the next Hop attributes of BGP. In order to be able to get the real response to changes in the route R3, you can configure the notification to route R3 on R4 and force the next hop to be R4 itself. The configuration is shown as below:
|
R4(config)#router bgp 64513 R4(config-router)#neighbor 10.1.1.1 next-hop-self |
13. Check the routing table of R3 once again, and confirm the configuration.
|
R3#show ip route
172.16.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets B 172.16.1.0 [200/0] via 10.1.1.2, 00:01:32 10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets C 10.1.1.0 is directly connected, Serial1/1 130.130.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets B 130.130.1.0 [200/0] via 10.1.1.2, 00:01:32 C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, Serial1/0 B 192.168.2.0/24 [200/0] via 10.1.1.2, 00:32:58 |
14. Use traceroute command to track the route information.
|
R3#traceroute 130.130.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort. Tracing the route to 130.130.1.1
1 10.1.1.2 92 msec 72 msec 72 msec 2 192.168.2.2 212 msec * 120 msec |
15. Use PING command to confirm the validity of the route.
|
R3#ping 130.130.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 130.130.1.1, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 96/130/168 ms |
16. Lab completed.
Hope to helpful for you!