Question 1
Which type of delay can lead to jitter in a voice network?
A. Propagation delay
B. Serialization delay
C. CODEC delay
D. Queuing delay
Answer: D
Question 2
IP phone A places a call to IP phone B. How many RTP streams are required for the call to be successfully completed?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 4
D. 6
Answer: B
Explanation:
Notice that RTP streams are one-way. If you are having a two-way conversation, the devices will establish dual RTP streams, one in each direction
Question 3
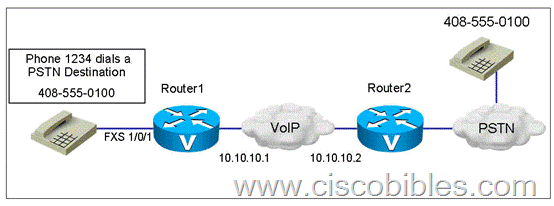
Refer to the exhibit.

The Acme Corporation needs assistance in configuring their PSTN voice gateway. Which two dial peers will correctly route calls to emergency services? (Choose two)
A. dial-peer voice 1 pots
destination-pattern 9911
port 1/0/0
B. dial-peer voice 911 pots
destination-pattern 911
forward-digits 3
port 1/0/1
C. dial-peer voice 9911 pots
destination-pattern 9911
forward-digits all
port 1/0/0
D. dial-peer voice 2 pots
destination-pattern 911
forward-digits 3
port 1/0/1
E. dial-peer voice 1 pots
destination-pattern 9911
prefix 911
port 1/0/0
F. dial-peer voice 2 pots
destination-pattern 911
forward-digits all
port 1/0/0
Answer: E F
Question 4
Approximately what percentage of voice packets can be dropped before voice quality becomes poor?
A. 1 to 2%
B. 15%
C. 5 to 10%
D. Less than or equal to 1%
Answer: D
Question 5
How does LLQ help ensure that voice quality is maintained in a converged network?
A. LLQ allocates minimum bandwidth guaranteed to voice traffic.
B. LLQ allocates a priority queue to voice traffic at a guaranteed rate.
C. LLQ allocates a priority queue and a minimum guaranteed bandwidth queue for voice.
D. LLQ ensures that all traffic is treated fairly and hence voice traffic is not severely impacted.
Answer: B
Explanation:
Low-latency queuing (LLQ) is used to give specific traffic classes higher priority when transmitting on the router’s WAN interface. Low Latency Queuing allows delay-sensitive data such as voice to be dequeued and sent first (before packets in other queues are dequeued), giving delay-sensitive data preferential treatment over other traffic.
The bandwidth given to an LLQ priority queue (PQ) is both the guaranteed minimum and policed maximum. This helps prevent the queue starvation that occurs with PQ.
Question 6
In which two situations would a voice gateway be required? (Choose two)
A. To connect a corporate or branch location to an IP WAN
B. To connect a corporate or branch location using VoIP to the PSTN
C. To connect a Cisco Unified Communications Manager to a LAN
D. To connect a Cisco Unified Communications network to a PBX
E. To connect a corporate or branch location to a MAN
Answer: B D
Question 7
What protocol is used to monitor and provide control information about the quality of an RTP session?
A. UDP
B. RTP
C. NTP
D. RTCP
Answer: D
Explanation:
RTCP is used to monitor and provide control information about the quality of RTP streams but notice that RTCP only provides feedback on the quality of the transmission link. It does not make any guarantees concerning quality of service.
Question 8
Which three are components of a dial plan? (Choose three)
A. Call legs
B. Endpoint addressing
C. centralized control
D. Call coverage
E. Digit manipulation
F. Decentralized control
Answer: B D E
Question 9
Refer to the exhibit.

The configuration shows a dial peer that points to Cisco Unity Express. Which line of configuration is incorrect?
A. B
B. C
C. D
D. E
E. F
F. G
Answer: E
Explanation:
We don’t have G.729ulaw, just G.711ulaw. G729 has 3 annexes that are G.729a, G.729b and G.729ab.
Question 10
Refer to the exhibit.
How many discrete call legs are needed to set up a call between the POTS phone attached to router 1 and the phone in the PSTN?
A. 3
B. 4
C. 6
D. 7
E. 8
F. 10
Answer: B
Explanation:
We need four call legs as shown below

Question 11
Refer to the exhibit.

Which inbound dial peer on CMERouter1 will be matched when phone extension 1234 places a call to 2010?
A. Voip dial peer 30
B. Default dial peer 30
C. None, which will cause the call to drop
D. Default dial peer
Answer: D
Explanation:
For CMERouter1 the “dial-peer voice 30 voip” will be matched for the outbound dial peer, not inbound one. When there is no dial-peer matched, the router will use the default dial peer.
Question 12
Refer to the exhibit.

Which two types of dial peers are needed to complete this call end-to-end? (Choose two)
A. Serial dial peer
B. PSTN dial peer
C. POTS dial peer
D. Network dial peer
E. VoIP dial peer
Answer: C E
Question 13
What is the relationship between a call leg and a dial peer?
A. A call leg is a virtual connection to set up a call whereas a dial peer is a physical connection to complete an end-to-end call.
B. The call leg and the dial peers are both logical connections used to complete an end-to-end call.
C. A call leg is a virtual connection that is set up and torn down before the dial peer is established.
D. The call leg and the dial peer are both physical connections used to complete an end-to-end call.
Answer: B
Question 14
Which type of voice port will be most cost effective to allow the gateway to terminate two circuits from the PSTN or a PBX?
A. FXO
B. FXS
C. PRI T1
D. E1
E. E&M
F. BRI
G. CAS T1
H. E1
Answer: E
Explanation:
For PSTN and PBX connection, we need to use an analog interface type. E&M signaling is designed to connect directly to a PBX system that also supports E&M interfaces. Many PBX brands have E&M analog trunk cards that can operate as either the trunk circuit side or the signaling unit side and Cisco gateway does support E&M interfaces.
Question 15
Which of the following is selected first for an incoming dial peer?
A. Answer-address
B. incoming called-number
C. destination-pattern
D. pots port
Answer: B
Question 16
Which protocol provides VoIP packet sequence numbering?
A. IP
B. TCP
C. UDP
D. RTP
Answer: D
Explanation:
The TCP protocol provides end-to-end network functions and delivery services for delay-sensitive, real-time data, such as voice and video. It runs on top of UDP and provides these services:
- Payload-type identification
- Sequence numbering
- Time stamping
- Delivery monitoring
Question 17
Identify the VoIP network component that provides CAC, bandwidth control and management, and address translation.
A. Gateway
B. Gatekeeper
C. MCU
D. Call agent
Answer: B
Question 18
Which three of the following are appropriate solutions to address latency issues in a VoIP network? (Choose 3)
A. Use dejitter buffers
B. Increase bandwidth
C. Fragment data packets
D. Prioritize voice packets
Answer: B C D
Explanation:
Notice that buffers give smoother audio playout but they does increase latency in VoIP network.
Question 19
Which three headers are compressed by cRTP? (Choose 3)
A. Data link
B. IP
C. UDP
D. RTP
Answer: B C D
Question 20
Which of the following best describes a function of RTCP?
A. RTCP provides encryption, message authentication and integrity, and anti-replay service for voice streams
B. RTCP uses even-numbered UDP ports in the range 16,384-32,767 to transport voice payloads
C. RTCP provides out-of-band control information for an RTP flow
D. RTCP caches an RTP packet’s Layer 3 and Layer 4 headers in the routers at each end of a link, resulting in lower bandwidth demand for subsequent RTP packets
Answer: C
Question 21
Which two of the following VoIP gateway platforms are considered to be Integrated Services Routers (ISRs)? (Choose two)
A. Cisco 2600XM Series
B. Cisco 2800 Series
C. Cisco 3700 Series
D. Cisco 3800 Series
Answer: B D