OSPF Network Topology Options
OSPF assumes a subnet is broadcast-capable by default.
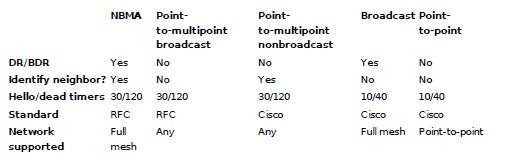
OSPF Network Types
Broadcast multiaccess
Point-to-point
Point-to-multipoint broadcast
Point-to-multipoint nonbroadcast
Nonbroadcast multiaccess (NBMA)
NBMA and point-to-multipoint are standards-compliant (RFC 2328), whereas point-to-multipoint nonbroadcast, broadcast, and point-to-point implementations are Cisco proprietary.
NBMA networks utilize DRs like broadcast networks, however neighbors must be manually defined instead of being automatically discovered.
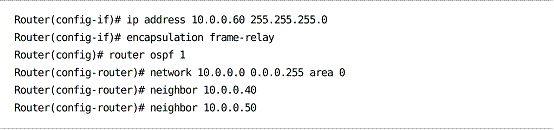
Configuring OSPF in a Nonbroadcast Environment
Nonbroadcast Network
Because NBMA is the default network type for a nonbroadcast interface, the only necessary
configuration is to define neighbors.
DR priorities should be specified to ensure only candidates positioned well in the topology are elected DR and BDR.
priority – This can be used to specify a higher priority than what has been configured on the neighbor (but not lower)
poll interval – The rate at which hellos are sent to inactive neighbors (default 120 seconds) cost – Cost to reach the neighbor
NBMA configuration:
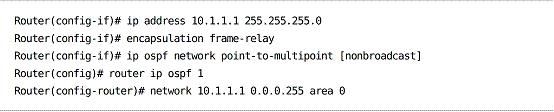
Point-to-multipoint Network
Point-to-multipoint automatically establishes adjacencies along PVCs.
Point-to-multipoint assumes broadcast capability by default; nonbroadcast can be specified, and neighbors must then be defined manually.
Broadcast Network
Point-to-point on Subinterfaces
Router(config)# interface serial0
Router(config-if)# no ip address
Router(config-if)# encapsulation frame-relay
Router(config)# interface serial0.1 point-to-point
Router(config-if)# ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)# frame-relay interface-dlci 51
Router(config)# interface serial0.2 point-to-point
Router(config-if)# ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)# frame-relay interface-dlci 52
Router(config)# router ip ospf 1
Router(config-router)# network 10.1.1.1 0.0.0.255 area 0